Why is a hard drive so slow?
Tuesday, 21. June 2011
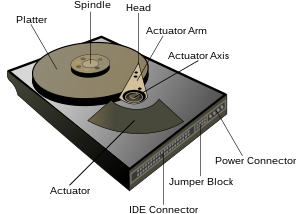
The answer is quite simple: A hard drive has moving parts.
In order for a hard drive to access or write data, it must be spinning (usually at 7,200 RPMs for a desktop computer, and 5400 for a laptop.)
Then, an arm must seek the track on the drive that you want to read or write to.
A hard drive only has one arm with a head attached to it. It can only read and write one track at a time.
Though the read and write access time of a drive is only a few miliseconds, there are thousands of seeks that must be performed to start a computer. And hundreds to open a file on a fragemented drive.
Drives such as Solid State have no moving parts, thus they are considerably faster.
Did this help you? Tell us how! Comment below.